
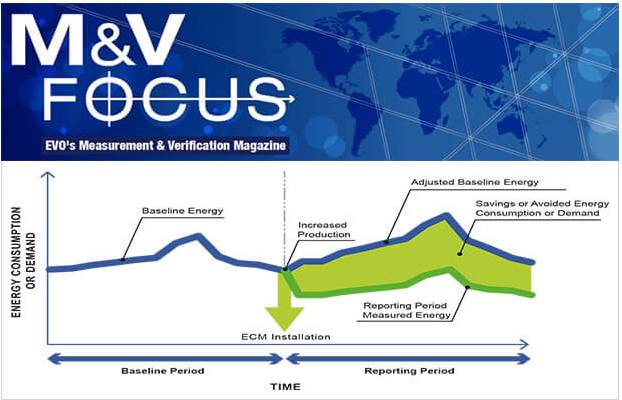
Monitoring & Verification (M & V) Audit under PAT
The basic objectives of the studies shall be to conduct Monitoring & Verification Audit by an Empaneled Accredited Energy Auditor (EMAEA), in accordance with the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Regulations, 2010 and furnish the report meeting all the mandatory requirements as stipulated in the regulations.
The audit shall be carried out as per the B E E guidelines and requirements and necessary certificates shall be issued. The audit shall cover
- Monitor & verify the Performance Assessment Document (PAD) or Form A along with all supporting information prepared by you as a fulfilment of the compliance requirement of the PAT scheme. The Verification shall be carried out as per the Monitoring & Verification guideline issued by BEE with special reference to Textile sector.
- During the process of M&V, we shall discuss and highlight its draft observations before finalizing the same.
- If any observations are made to modify the prepared document, we shall provide adequate time to enable you for modification/rectification.
- We shall discharge the responsibility of verification in a consultative manner with you or your representatives; while following the guidelines/protocol for M & V as issued by BEE.
- After satisfactory verification of all the data/documents, we shall submit the verification report i.e. Form-B to Century Rayon with due signature of the AEA. This verification report shall be submitted within 5 days from the conclusion of all the M & V activities.
The basic objectives of the studies shall be to conduct energy audit by an accredited energy auditor, in accordance with the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Regulations, 2010 and furnish the report meeting all the mandatory requirements as stipulated in the regulations.
The Mandatory Energy Audit is conducted as per the BEE requirements and cover
- Production process description
- Brief description of manufacturing process
- Process flow diagram and major unit operations
- Major raw material inputs, quantity & costs
- Energy & utility system description
- List of utilities
- Brief description of utility
- Detail process flow diagram and Energy & Material Balance
- Flow Chart showing flow rate, temperature & pressure of all input / output streams
- Water balance for entire industry
- Energy balance of the designated consumer in tabular form
- Performance evaluation of major utility and process equipments / systems
- List of equipments & processes where performance testing was done
- Results of performance testing
- Energy efficiency in utility and process system
- Specific Energy Consumption
- Boiler Efficiency Assessment
- Thermic fluid heater performance assessment
- Furnace / kiln efficiency analysis
- Cooling water system performance assessment
- Diesel generator set performance assessment
- Refrigeration system performance assessment
- Compressed air system performance assessment
- Electrical motor load analysis
- Lighting system
- Others
- Evaluation of energy management system
- Energy management policy
- Energy management monitoring system
- Development and establishment of procedure include energy efficiency possibilities
- Benchmarking
- Training of staff responsible for operational & associated processes vi.General audit review vii.Conform to acts, rules and regulations framed thereunder viii.Strength and weakness of the designated consumer
- Energy conservations measures & recommendations management system
- The report shall provide existing energy profile of the designated consumer with percentage share of major equipments, process, utilities so that it becomes a basic document for future monitoring
- Details of energy conservation measures recommended in Form 2
- Cost benefit analysis of each recommended energy saving measures as per the standard practice
- The investment proposals shall be backed with technical and economic viability and prioritization on energy conservation measures based on financial analysis of various options taking in to account the capacity of the designated consumer to make investment in such measures.
- The energy auditor may also consider the substitutions of existing energy use by any other form of techno-commercially viable form of energy
- Details of energy saving measures implemented, investment made and saving in energy achieved together with progress made in the implementation of the remaining energy saving measures in Form 3.
- Report
- The report shall be prepared in the required formats and as per the guidelines and duly signed by an Accredited Energy Auditor.
a. Electricity b. Stream c. Water d. Compressor Air e. Chilled Water f. Colling Water g. Others
BENEFITS OF ENERGY AUDIT
- Aids in Cost Optimization
- Operating Advantages
- Reduction in Energy Wastage
- Intangible Benefits
- Sustainability and Environment Protection
A thorough energy audit done with sophisticated instruments and methods analyses the system in detail and provides cost-effective solutions to reduce your utility bills. For instance, A comprehensive Energy Audit takes into account a building’s air conditioning system and its internal structure and figures out how the interconnected system works, finding leakages and unwanted heat transmission. It then recommends ways for maximizing functionality and minimizing expenses.
Apart from monetary gains, Energy Audit helps your business in designing a highly efficient system by modernizing building’s structure both internally and externally based on energy-friendly techniques. It will certainly decrease operational cost, enhance operational capacity, give longevity to equipment life.
Energy Audits helps your business save money by reducing energy wastage. As it identifies the sources of maximum energy inefficiency and, in turn, wasting the maximum money. And after contemplating the utility and non-utility monetary gains, energy efficiency solutions are implemented for the reduction of energy waste and improved output/productivity.
The merits of the energy-efficient building go beyond increased asset valuation and sustainability. The long term rewards are associated with creating a “green” business image in the market, enhancing customer loyalty and brand recognition and improved employee productivity and morale.
The purpose of an energy audit is not limited to cost-cutting and operational productivity for any business. Be it a small-scale or a large scale industry, Energy audit while serving its purpose helps in protecting the environment. It aids in reducing fossil-fuel pollution and thus ensuring the security of energy for future generations.
